Characteristics of Cloud Computing
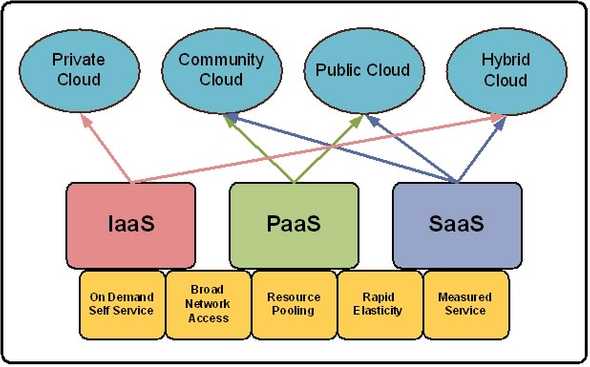
On-demand self service
Cloud computing resources can be provisioned on-demand by the users, without requiring interactons with the cloud service provider. The process of provisioning resources is automated.
Broad network access
Cloud computing resources can be accessed over the network using standard access mechanisms that provide platform-independent access through the use of heterogeneous client platforms such as workstations, laptops, tablets and smartphones.
Resource pooling
The computing and storage resources provided by cloud service providers are pooled to serve multiple users using multi-tenancy. Multi-tenancy aspects of the cloud allow multiple users to be served by the same physical hardware. Users are assigned virtual resources that run on top of the physical resources.
Rapid elasticity
Cloud resources ca be rapidly scaled up or down based on demand. Two types of scaling options exists:
Horizontal Scaling (scaling out)
Horizontal scaling or scaling-out involves launching and provisioning additional server resources.
Vertical Scaling (scaling up)
Vertical scaling or scaling-up involves changing the computing capacity assigned to the server resources while keeping the number of servers resources constant
Meaured service
Cloud computing resources are provided to users on a pay-per-use model. Metrics such as amount of CPU cycles used, amount of storage space used, number of network I/O requests, etc. are used to calculate the usage charges of the cloud resources.
Performance
Cloud computing provides improved performance for applications since the resources available to the application can be scaled up or down based on the dynamic application workloads.
Reduced costs
Cloud computing provides cost benefits for applications as only as much computing and storage resources as required can be provisioned dynamically, and upfront investment in purchase of computing assets to cover worst case requirements is avoid.
Outsorced Managment
Cloud computing allows the users to outsource the IT infrastructure requirements to external cloud providers.
Reliability
Applications deployed in cloud computing environments generally have a higher reliability since the underlying IT infrastructure is professionally managed by the cloud service. Most cloud providers delivers a SLA (service level agreements) with promise of 99.99% uptime guarantee for the cloud resources, witch may often be expensive to achieve with in-house IT infrastructure.
Multi-tenancy
The multi-tenanted approach of the cloud allows multiple users to make use of the same shared resources. Multi-tenanct can be of different forms:
Virtual multi-tenancy
In virtual multi-tenancy, computing and storage resources are shared among multiple users. Multiple tentant are served from virtual machines (VMs) that execute concurrently on top of the same computing and storage resources.
Organic multi-tenancy
In a organic multi-tenancy every component in the system architecture is shared among multiple tentants, including hardware, OS, database servers, application servers, load balances, etc. Organic multi-tenancy exists when explicit multi-tenant design patterns are coded into the application.
Cloud Models
Service Models
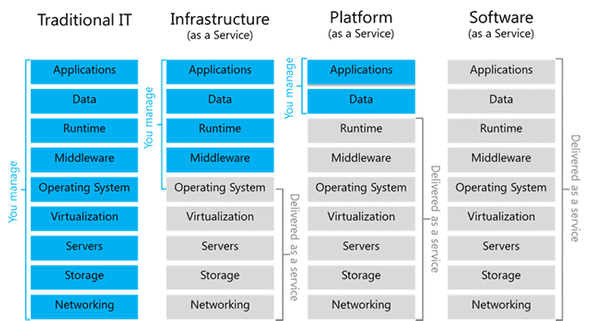
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides the users the capability to provision computing and storage resources. These resources are provided to the users as virtual machines instances and virtual storage. Users can start, stop, configure and manage the virtual machine instances and virtual storage.Users can deploy operating systems and applications of their choise on the virtual resources provisioned in the cloud. The cloud service provider manages the underlying infrastructure. The users are billed on the pay-per-useparadigm. Common metering used are the number of virtual machines hours used and/or the amount of storage space provisioned.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides the users the capability to develop and deploy application in the cloud using the development tools, application programming interfaces (API’s), software libraries and services provided by the cloud service provider. The cloud service provider manages the underlying cloud infrastructures including servers, network, operating systems and storage. The users, themselves, are repsonsible for developing, deploying, configuring and managing applications on the cloud infrastructure.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides the users a complete software appliation or the user interface to the application itself. The cloud service provider manages the underlying cloud infrastructure including servers, network, operating systems, storage and application software, and the user is unaware of the underlying architecture of the cloud. Applications are privided to the user through a thin client interface (e.g., a browser)
Deployment Models
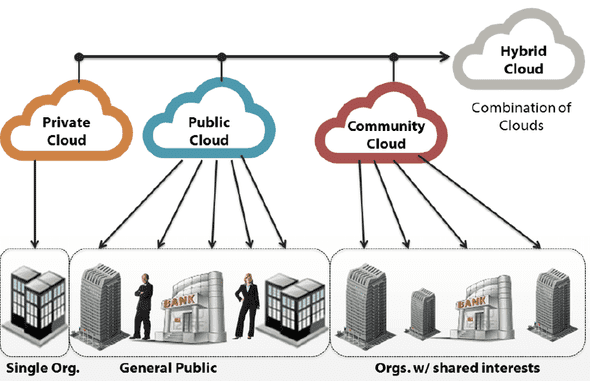
Public cloud
In the public deployment model, cloud services are available to the general public or a large group of companies. The cloud resources are shared among different users. The cloud services are provided by a third.party cloud provider. Public clouds are best suited for users who want to use cloud infrastructure for development and testing of applications and host applications in the cloud toserve large workloads, without upfront investments in IT infrastructure.
Private cloud
In the private cloud deployment model cloud infrastructure is operated for exclusive use of a single organization. Private cloud services are dedicated for a single organization. Cloud infrastructure can be setup on premise or off-premise and may be managed internally or by a third-party. Private clouds are best suited for applications where security is very important and organizations that want to have very tight control over their data.
Hybrid cloud
The hybrid cloud deployment model compines the services of multiple clouds (private or public). The individuals retain their unique identities but are bound by standarized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability. Hybrid clouds are best suited for organizations that want to take advantage og secured application nd data hosting on a private cloud, and at the same time benefit from cost savings by hosting shared applications and data in public clouds.
Community cloud
In the community cloud deployment, the cloud services are shared by several organizations that have the same policy and compliance considerations. Community clouds are best suited for organizations that want access to the same applications and data, and want the cloud costs to be shared with the larger group.
Cloud Concepts and Technologies
Virtualization
Virtualixation refers to the partitioning the resources of a physical systeminto mulitple virtual resources. Virtualization is the key enabling techology if cloud computing and allows pooling of resources. In cloud computing, resources are pooled to serve mulitple users using multi-tenancy. Multi-tenant aspect of the cloud allow multiple users to be served by the same physical hardware. The virtualization layer allows multiple operating system instances to run currently as virtual machines on the same underlying physical resources.
Hypervisor
The virtualization layer consists of a hypervisor or a virtual machine monitor (VMM) The hypervisor presents a virtual operating platform to a guest operating system (OS). There are two types of hypervisors:
Type-1 hypervisors
Type-1 hypervisors or native hypervisors run directly on the host hardware and control the hardware and monitor the guest operating systems.
Type-2 hypervisors
Type-2 hypervisors or hosted hypervisors run on top of a conventional (main/host) operating system and monitor the guest systems.
Guest OS
A guest OS is an operating system that is installed in a virtual machine in addition to the host or main OS. In virtualization, the guest OS can be different from the host OS.
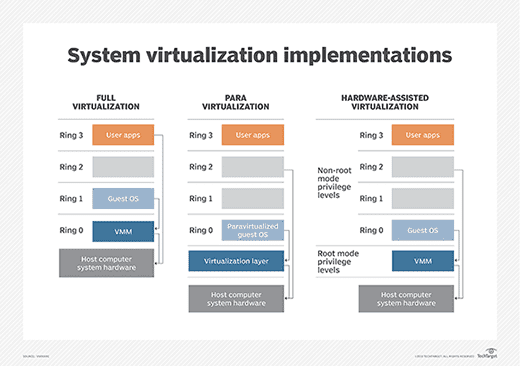
Full virtualization
In full virtualization, the virtualization layer completley decouples the guest OS from the underlying hardware. The guest OS requires no modification and is not aware that it is being virtualized. Full virtualization is enabled by direct execution of user requests and binary translation of OS requests.
Para-virtualization
In para-virtualization the guest OS is modified to enable communication with the hypervisor to improve performance and efficiency. The guest OS kernel is modified to replace non-virtualizable instructions with hypercalls that communicate directly with the virtualization layer hypervisor.
Hardware virtualization
Hardware assisted virtualization is enabled by hardware features such as Intel’s Virtualization Technology (VT-x) and AMD’s AMD-V. In hardware assisted virtualization, privileged and sensitive calls are set to automatically trap to the hypervisor. Thus, there is no need for either inary ranslation or para-virtualization.
Load balancing
Load balancing distribute workloads across mulitple servers to meet the application workloads. The goal if load balancing techinque are to achieve maximum utilization of resources, minimizing he response times, maximizing throughput. Load balancing distribute the incomming user requests aross mulitiple resources. To the end user accessing a cloud-basd application, a load balancer makes the pool of servers under the load balancer appear as a single server with high computing capacity. The routing of user requests is determined based on a load balancing algorithm, Comonly used load balancing algorithms include:
| Algorithm | Description |
|---|---|
| Round Robin | The servers are selected one by one to serve the incomming requests in a non-hierarchial circular fashion with no priority assigned to a specific server. |
| Weighted Round Robin | Servers are assigned some weights. The incomming requests are proportionally routed using a static or dynamic ratio of respective weights. |
| Low Latency | The load balancer monitors the latency of each server. Each incoming request is routed to the server whitch has the lowest latency. |
| Least Connections | The incoming requests are routed to the server with the least number of connections. |
| Priority | Each server is assigned a proprity. The incomming traffic is routed to the highest priority server as long as the server is available. When the highest priority server fails, the incomming traffic is routed to a server with a lower priority. |
| Overflow | Similar to priority load balancing. When the incomming requests to highest priority server overflow, the requests are routed to a lower priority server. |
For session based applications, an important issue to handle during load balancing is the persistence of multiple requests from a particular user session. ince load balancing can route successive requests from a user session to different servers, maintaining the state or the information of the session is important.
| Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Sticky sessions | All requests belonging to a user session are routed to the same server. Solution is simple to manage, the drawback of this approach is that if a server fails all the sessions belonging to that server is lost. |
| Session Database | All the session information is stored externally in a seperate session database, which is often replicated to avoid single point of failure. But the approach involves additional overhead storing the session information, however this approach allows automatic failover. |
| Browser cookies | The session information is stored on the client side in form of a cookie. The benefit of this approach is that it makes session managment east and has the least amount of overhead for the load balancer. |
Replication
Replication is used to create and maintain multiple copies of the data in the cloud. Replication of data is important for practical reasins such as business continuity and disaster recovery. Cloud based data replication approaches provide replication of data in multiple locations, automated recovery, low recovery point objective (RPO) and low recovery tume objective (RTO). Cloud provides affordable replication solutions with pay-per-use/pay-as-you-go pricing models.
Array-based Replication
Array-based replication uses compatible storage arrays to automatically copy data from a local storage array to a remote storage array. Arrays replicate data at the disk sub-system level, therefore the type of hosts accessing the data and the type of data is not important. Array-based replication usese Network Attached Storage (NAS) or Storage Area Network (SAN), to replicate. A drawback of this approach is that it requires similar arrays at local and remote locations. Therefore the cost for setting up array-based replication are higher that the other approaches.
Network-based Replication
Network-based replication uses an appliance that sits on the network and interceots packets that are send from hosts and storage arrays. The inercepted packets are replicated to a secondary location. The benefits of this approach is that it supports heterogeneous environments and require a single point of managment. However, this approach involves higher initial costs due to replication hardware and software.
Host-based Replication
Host-based replication runs on standard servers and uses software to transfer data from a local to remote location. The host acts the replication control mechanism. An agent is installed on the hosts that communicate with the agents on the other hosts. Host-based replication can either be block-based or file-based. Host-based replication with cloud-infrastructure provides affordable replication solutions. With host-based replication, entire virtual machines can be replicated in real-time.
Monitoring
Cloud resources can be monitored by monitoring services provided by the cloud service providers. Monitoring services allow cloud users to collect and analyze the data on various monitoring metrics. Monitoring of cloud resources is important because it allows the users to keep track of the health of applications and services deployed in the cloud. With metrics available at run-time users can make operational decisions such as scaling up or scaling down cloud resources.
| Type | Metrics |
|---|---|
| CPU | CPU-Usage, CPU-Idle |
| Disk | Disk-Usage, Bytes/sec (read/write), Operations/sec |
| Memory | Memory-USed, Memory-Free, Page-Cache |
| Interface | Packets/sec (incoming, outgoing), Octets/sec (incoming/outgoing) |
Software Defined Networking (SDN)
A SDN is a networking architecture that separates the control plane from the data plane and centralies the network controller. In the conventional network architecture the control plane and data plane are coupled. Control plane is the part of the network that carries the payload data traffic. The limitations of the conventional network architecture are as follows:
Complex Network Devices
The conventional networks were well suited for static traffic pattern and had a large number of protocols designed for specific applications. With the emergence of cloud computing and proliferation of internet access devices, the traffic patterns are becoming more and more dynamic. Due to the complexity of conventional network devices, making changes in the networks to meet the dynamic traffic pattern has become increasingly difficult.
Managment Overhead
Conventional networks involce significant management overhead. Upgradation of network requires configuration changes in multiple devices and interfaces from multiple vendors. (switches, routers, firewalls, etc.).
Limited Scalability
The virtualization technologies used in cloud computing environments has increased the number of virtual hosts requiring network access (Big data application generate a lot of data between VM’s). Such computing environments require highly scalable and easy to manage network architectures with minimal configurations, which is becoming increasingly difficult with conventional networks.
SDN attempts to create network architectures that are simpler, inexpensive, scalable, agile and easy to manage. Software-based SDB controllers maintain a unified view of the network and make configuration, managment and provisioning simpler. The underlying network infrastructure is abstracted from the applications. Network devices become simple with SDN as they do not require implementations of a large number of protocols. Network devices recieve instructions from the SDN controller on how to forward the packets. These devices can be simpler and cost less as they can be built from standard hardware and software components.
Key elements of SDN as as follows:
Centralized Network Controller
With decoupled the control and data planes and centralized network controller, the network administrators can rapidly configure the network.
Programmable Open API’s
SDN supports programmable open API’s for interface between the SDN application and control layers. These open API’s allow impementing various network services such as routing, quality of service (QoS), access control, etc.
Standard Communication Interface (OpenFlow)
SDN uses a standard communication interface between the control and infrastructure layers that is called OpenFlow. OpenFlow uses the concept of flows to identify network traffic based in pre-defined match rules.
MapReduce
Identity and Access Managment
Service Level Agreements (SLA)
A Service Level Agreement for cloud specifies the level of service that is formally defined as a part of the service contract with the cloud service provider. SLAs provide a level of service for each service which is specified in the form of minimum level of service guaranteed and a target level. SLAs contain a number of performance metrics and the corresponding service level objectives.
| Criteria | Details |
|---|---|
| Availability | Percentage of time the service is guaranteed to be available |
| Performance | Response time, Throughput |
| Disaster Recovery | Mean time to recover |
| Problem resolution | Process to identify problems, support options, resolution expectations |
| Security and privacy of data | Machanism for security of data in storage and transmission |
Billing
Cloud service providers offer a number of billing models described as follows:
Elastic Pricing
Pay-as-you-use pricing model, the customers are charged based on the usage of cloud resources. Cloud computing provides the benefit of provision resources on-demand. A good model for customers who cannot predict the usage beforehand, or for a short time usage of a cloud resource.
Fixed Pricing
Customers are charged a fixed amount per month for the cloud resource. For example, fixed amount can be charged per month for running a virtual machine instance, irrespactive of the actual usage. Suited for customers who want more control over the cloud expenses.
Spot Pricing
Offer variable pricing for cloud resources which is driven by the marked demand. When the demand for cloud resources is high the prices increase, or when the demand is low the prices decrease.